The food we eat plays a significant role in our mental health and emotional well-being. While balanced nutrition has long been recognized for its physical health benefits, recent research highlights how certain foods can positively impact mood, reduce anxiety, and support overall mental health. By incorporating specific nutrients into our diets, we can support brain function, stabilize mood, and enhance resilience to stress.
This article explores the connection between diet and mental health, focusing on foods that boost mood and help manage anxiety. By understanding the impact of nutrition on the mind, you can make dietary choices that support your mental well-being and foster a healthier relationship with food.
Understanding the Link Between Nutrition and Mental Health
How Diet Affects Mood and Brain Function
Our brain requires a steady supply of nutrients to function optimally, and the quality of these nutrients directly affects brain chemistry, energy levels, and emotional stability. Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants influence neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and cognition. Consuming a balanced diet helps support these neurotransmitters, making it easier to manage stress and stay focused.
By maintaining stable blood sugar levels through balanced meals, we can also prevent energy dips that often contribute to irritability and mood swings. A nutritious diet lays the foundation for better mental health, making it easier to cope with daily stressors.
The Role of Gut Health in Mental Well-Being
The gut-brain connection, often referred to as the “second brain,” is a powerful link between digestive health and mental health. The gut produces many neurotransmitters, including serotonin, which is associated with mood regulation. A healthy gut environment, supported by probiotics and fiber, fosters balanced neurotransmitter production, positively impacting mood and reducing anxiety.
By supporting gut health through a fiber-rich, balanced diet, we can improve mental resilience and emotional stability, as well as support cognitive function.
For insights into the relationship between diet and mental health, explore this article on PubMed Central. The study highlights how dietary patterns rich in neuroactive compounds, such as polyphenols and omega-3 fatty acids, can positively influence brain health and emotional well-being.
Nutritional Deficiencies Linked to Anxiety and Depression
Certain nutritional deficiencies are commonly associated with mental health issues. For example, low levels of B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and magnesium have been linked to increased anxiety and depressive symptoms. Addressing these deficiencies through diet can have a noticeable effect on mood and mental clarity.
By understanding which nutrients play a key role in mental health, you can incorporate more of these into your diet, helping reduce symptoms of anxiety and improve overall mood.

Mood-Boosting Foods to Include in Your Diet
1. Omega-3 Rich Foods
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health, playing a role in reducing inflammation and supporting cognitive function. Research shows that omega-3s can improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety by influencing neurotransmitters like serotonin.
Sources of omega-3s: Fatty fish (such as salmon and sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are excellent sources of omega-3s. Aim to include these foods in your diet a few times a week for optimal brain support.
2. Whole Grains and Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, help regulate blood sugar levels, which can have a stabilizing effect on mood. Unlike refined carbs that cause quick spikes and crashes in blood sugar, complex carbs provide sustained energy, reducing irritability and promoting focus.
Examples of complex carbs: Oats, quinoa, brown rice, and sweet potatoes. Incorporating these foods into meals can help maintain steady energy levels and support mental clarity throughout the day.
3. Leafy Greens and Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium is a mineral that promotes relaxation and is often referred to as “nature’s relaxant.” Low magnesium levels have been linked to anxiety, so including magnesium-rich foods can help you feel calmer and more at ease.
Sources of magnesium: Spinach, kale, almonds, pumpkin seeds, and dark chocolate. Incorporating leafy greens and other magnesium-rich foods can support mental relaxation and reduce stress.
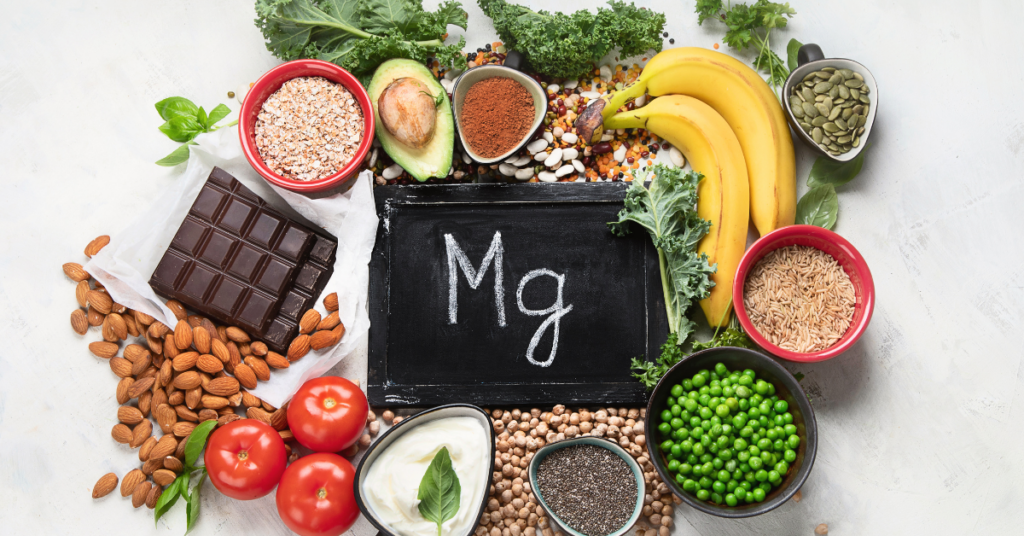
Foods That Help Reduce Anxiety and Promote Calm
Probiotic-Rich Foods for Gut Health
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health, which in turn benefits mental well-being. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, probiotics can help regulate mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety.
Sources of probiotics: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented foods. Adding these foods to your diet helps maintain gut health, which can support a balanced mood and reduce stress.
Vitamin B-Rich Foods for Brain Function
B vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, are essential for brain health and energy. These vitamins support the nervous system, helping manage stress and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Sources of B vitamins: Eggs, lentils, leafy greens, and fortified cereals. Including B-vitamin-rich foods in your diet helps support brain function and emotional well-being.
Herbal Teas and Calming Foods
Certain herbal teas have natural calming effects, helping reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Chamomile tea, for example, is known for its soothing qualities, while green tea contains L-theanine, an amino acid that supports relaxation without causing drowsiness.
Other calming foods: Turkey (contains tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin) and avocados (contain healthy fats for brain function). Sipping herbal tea and incorporating calming foods into your diet can help you unwind and feel more relaxed.

Dietary Tips for Supporting Mental Health
Eating Regular, Balanced Meals
Consuming regular, balanced meals helps prevent blood sugar fluctuations that can affect mood and energy levels. Aim to include a source of protein, healthy fat, and complex carbs in each meal to support steady energy and mental clarity.
Regular meals also help prevent the energy dips that often lead to irritability or stress, supporting a more stable mood throughout the day.
For a comprehensive look at how nutrition impacts mental well-being, visit Diet and Mental Health from the Mental Health Foundation. This guide explores the connection between what you eat and how you feel, offering practical tips for a healthier mind and body.
Staying Hydrated for Better Brain Function
Hydration is crucial for optimal brain function, as even mild dehydration can affect concentration, mood, and energy. Staying hydrated improves mental focus and helps regulate mood, making it easier to manage stress.
Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, and consider increasing intake if you’re active or live in a warm climate.
Limiting Sugar and Processed Foods
High sugar intake and processed foods are linked to mood swings and increased stress levels. Excessive sugar causes rapid blood sugar spikes and crashes, which can lead to irritability and fatigue. Processed foods, often high in refined carbs and unhealthy fats, may also negatively impact mood and energy.
Opt for whole foods over processed ones whenever possible, choosing fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins for sustained mental clarity and stable energy.

Creating a Sustainable Diet for Mental Health
Planning and Preparing Mood-Boosting Meals
Planning meals ahead can help ensure you have nutrient-dense foods available throughout the week. Incorporate mood-boosting foods like leafy greens, whole grains, and omega-3-rich sources into your meal prep, making it easy to maintain balanced eating habits even on busy days.
By having these foods ready to go, you’re more likely to make healthy choices that support both physical and mental well-being.
Listening to Your Body and Avoiding Extreme Diets
A sustainable diet for mental health should focus on balance and variety rather than restriction. Extreme or overly restrictive diets can increase stress and may lead to nutritional deficiencies that impact mood. Instead, aim for a balanced, nutrient-rich diet that supports both body and mind.
Listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues helps create a healthier, more enjoyable relationship with food, promoting a positive impact on mental health.
For advice on maintaining balanced eating habits, check out Avoid the Extremes of Hunger and Fullness from Nutrition in Recovery. This article provides tips for achieving a healthy relationship with food and supporting overall well-being.
Incorporating Enjoyable Foods Without Guilt
Allowing yourself to enjoy foods you love, even if they’re not always “healthy,” can reduce stress around eating and improve your relationship with food. Incorporate comfort foods mindfully, savoring each bite, and balancing them with nutrient-dense options.
This approach promotes mental flexibility and helps reduce guilt, making it easier to maintain a balanced diet that supports both mood and well-being.
Nutrition plays a powerful role in supporting mental health, and by incorporating mood-boosting foods into your diet, you can help manage stress, reduce anxiety, and improve focus. Foods rich in omega-3s, probiotics, magnesium, and B vitamins provide essential nutrients for brain health, while balanced meals and regular hydration support emotional stability.
By taking small steps to include these foods in your daily diet, you can enjoy the mental and emotional benefits of better nutrition. Remember, a balanced approach to eating is key to fostering a healthy mind and a healthy relationship with food.
For a simple yet powerful way to improve your emotional well-being, explore our guide on Gratitude Journaling toBoost Mental Wellness. Learn how daily gratitude practices can foster positivity and enhance mental health.






















Comments 1